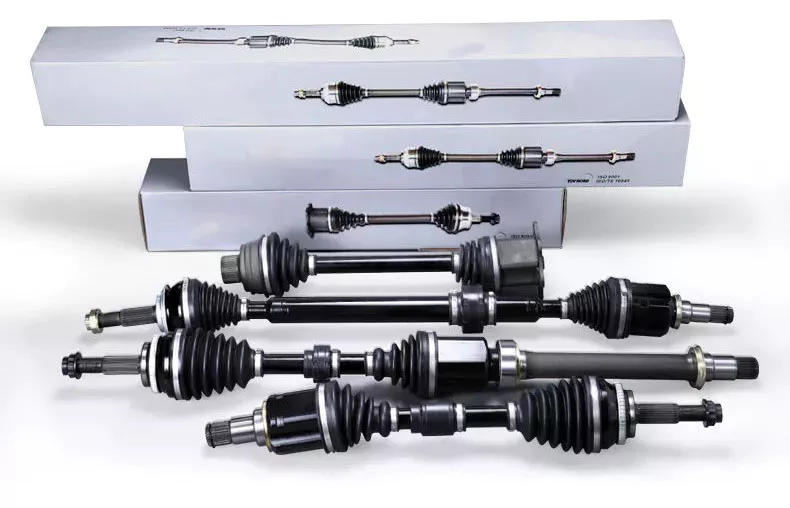
Product Description
Product Description
Product Parameters
| Item | Spur Gear Axle Shaft |
| Material | 4140,4340,40Cr,42Crmo,42Crmo4,20Cr,20CrMnti, 20Crmo,35Crmo |
| OEM NO | Customize |
| Certification | ISO/TS16949 |
| Test Requirement | Magnetic Powder Test, Hardness Test, Dimension Test |
| Color | Paint , Natural Finish ,Machining All Around |
| Material | Aluminum: 5000series(5052…)/6000series(6061…)/7000series(7075…) |
| Steel: Carbon Steel,Middle Steel,Steel Alloy,etc. | |
| Stainess Steel: 303/304/316,etc. | |
| Copper/Brass/Bronze/Red Copper,etc. | |
| Plastic:ABS,PP,PC,Nylon,Delrin(POM),Bakelite,etc. | |
| Size | According to Customer’s drawing or samples |
| Process | CNC machining,Turning,Milling,Stamping,Grinding,Welding,Wire Injection,Cutting,etc. |
| Tolerance | ≥+/-0.03mm |
| Surface Treatment | (Sandblast)&(Hard)&(Color)Anodizing,(Chrome,Nickel,Zinc…)Plating,Painting,Powder Coating,Polishing,Blackened,Hardened,Lasering,Engraving,etc. |
| File Formats | ProE,SolidWorks,UG,CAD,PDF(IGS,X-T,STP,STL) |
| Sample | Available |
| Packing | Spline protect cover ,Wood box ,Waterproof membrane; Or per customers’ requirements. |
Our Advantages
Why Choose US ???
1. Equipment :
Our company boasts all necessary production equipment,
including Hydraulic press machines, Japanese CNC lathe (TAKISAWA), Korean gear hobbing machine (I SNT), gear shaping machine, machining center, CNC grinder, heat treatment line etc.
2. Processing precision:
We are a professional gear & gear shafts manufacturer. Our gears are around 6-7 grade in mass production.
3. Company:
We have 90 employees, including 10 technical staffs. Covering an area of 20000 square meters.
4. Certification :
Oue company has passed ISO 14001 and TS16949
5.Sample service :
We provide free sample for confirmation and customer bears the freight charges
6.OEM service :
Having our own factory and professional technicians,we welcome OEM orders as well.We can design and produce the specific product you need according to your detail information
Cooperation Partner
Company Profile
Our Featured Products
/* January 22, 2571 19:08:37 */!function(){function s(e,r){var a,o={};try{e&&e.split(“,”).forEach(function(e,t){e&&(a=e.match(/(.*?):(.*)$/))&&1
| Material: | Alloy Steel |
|---|---|
| Load: | Drive Shaft |
| Axis Shape: | Straight Shaft |
| Appearance Shape: | Round |
| Rotation: | Cw |
| Yield: | 5, 000PCS / Month |
| Samples: |
US$ 0/Piece
1 Piece(Min.Order) | |
|---|
| Customization: |
Available
| Customized Request |
|---|
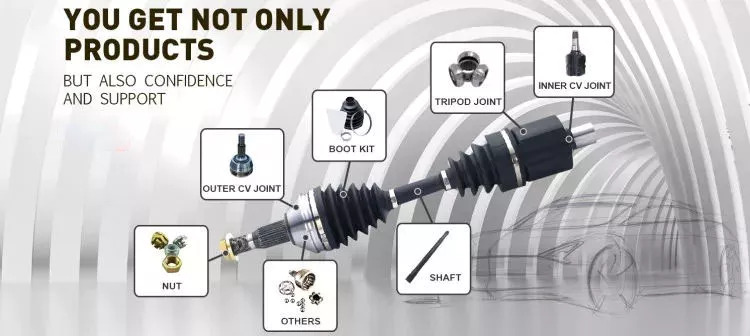
How do drive shafts ensure efficient power transfer while maintaining balance?
Drive shafts employ various mechanisms to ensure efficient power transfer while maintaining balance. Efficient power transfer refers to the ability of the drive shaft to transmit rotational power from the source (such as an engine) to the driven components (such as wheels or machinery) with minimal energy loss. Balancing, on the other hand, involves minimizing vibrations and eliminating any uneven distribution of mass that can cause disturbances during operation. Here’s an explanation of how drive shafts achieve both efficient power transfer and balance:
1. Material Selection:
The material selection for drive shafts is crucial for maintaining balance and ensuring efficient power transfer. Drive shafts are commonly made from materials such as steel or aluminum alloys, chosen for their strength, stiffness, and durability. These materials have excellent dimensional stability and can withstand the torque loads encountered during operation. By using high-quality materials, drive shafts can minimize deformation, flexing, and imbalances that could compromise power transmission and generate vibrations.
2. Design Considerations:
The design of the drive shaft plays a significant role in both power transfer efficiency and balance. Drive shafts are engineered to have appropriate dimensions, including diameter and wall thickness, to handle the anticipated torque loads without excessive deflection or vibration. The design also considers factors such as the length of the drive shaft, the number and type of joints (such as universal joints or constant velocity joints), and the use of balancing weights. By carefully designing the drive shaft, manufacturers can achieve optimal power transfer efficiency while minimizing the potential for imbalance-induced vibrations.
3. Balancing Techniques:
Balance is crucial for drive shafts as any imbalance can cause vibrations, noise, and accelerated wear. To maintain balance, drive shafts undergo various balancing techniques during the manufacturing process. Static and dynamic balancing methods are employed to ensure that the mass distribution along the drive shaft is uniform. Static balancing involves adding counterweights at specific locations to offset any weight imbalances. Dynamic balancing is performed by spinning the drive shaft at high speeds and measuring any vibrations. If imbalances are detected, additional adjustments are made to achieve a balanced state. These balancing techniques help minimize vibrations and ensure smooth operation of the drive shaft.
4. Universal Joints and Constant Velocity Joints:
Drive shafts often incorporate universal joints (U-joints) or constant velocity (CV) joints to accommodate misalignment and maintain balance during operation. U-joints are flexible joints that allow for angular movement between shafts. They are typically used in applications where the drive shaft operates at varying angles. CV joints, on the other hand, are designed to maintain a constant velocity of rotation and are commonly used in front-wheel-drive vehicles. By incorporating these joints, drive shafts can compensate for misalignment, reduce stress on the shaft, and minimize vibrations that can negatively impact power transfer efficiency and balance.
5. Maintenance and Inspection:
Regular maintenance and inspection of drive shafts are essential for ensuring efficient power transfer and balance. Periodic checks for wear, damage, or misalignment can help identify any issues that may affect the drive shaft’s performance. Lubrication of the joints and proper tightening of fasteners are also critical for maintaining optimal operation. By adhering to recommended maintenance procedures, any imbalances or inefficiencies can be addressed promptly, ensuring continued efficient power transfer and balance.
In summary, drive shafts ensure efficient power transfer while maintaining balance through careful material selection, thoughtful design considerations, balancing techniques, and the incorporation of flexible joints. By optimizing these factors, drive shafts can transmit rotational power smoothly and reliably, minimizing energy losses and vibrations that can impact performance and longevity.

Can drive shafts be customized for specific vehicle or equipment requirements?
Yes, drive shafts can be customized to meet specific vehicle or equipment requirements. Customization allows manufacturers to tailor the design, dimensions, materials, and other parameters of the drive shaft to ensure compatibility and optimal performance within a particular vehicle or equipment. Here’s a detailed explanation of how drive shafts can be customized:
1. Dimensional Customization:
Drive shafts can be customized to match the dimensional requirements of the vehicle or equipment. This includes adjusting the overall length, diameter, and spline configuration to ensure proper fitment and clearances within the specific application. By customizing the dimensions, the drive shaft can be seamlessly integrated into the driveline system without any interference or limitations.
2. Material Selection:
The choice of materials for drive shafts can be customized based on the specific requirements of the vehicle or equipment. Different materials, such as steel alloys, aluminum alloys, or specialized composites, can be selected to optimize strength, weight, and durability. The material selection can be tailored to meet the torque, speed, and operating conditions of the application, ensuring the drive shaft’s reliability and longevity.
3. Joint Configuration:
Drive shafts can be customized with different joint configurations to accommodate specific vehicle or equipment requirements. For example, universal joints (U-joints) may be suitable for applications with lower operating angles and moderate torque demands, while constant velocity (CV) joints are often used in applications requiring higher operating angles and smoother power transmission. The choice of joint configuration depends on factors such as operating angle, torque capacity, and desired performance characteristics.
4. Torque and Power Capacity:
Customization allows drive shafts to be designed with the appropriate torque and power capacity for the specific vehicle or equipment. Manufacturers can analyze the torque requirements, operating conditions, and safety margins of the application to determine the optimal torque rating and power capacity of the drive shaft. This ensures that the drive shaft can handle the required loads without experiencing premature failure or performance issues.
5. Balancing and Vibration Control:
Drive shafts can be customized with precision balancing and vibration control measures. Imbalances in the drive shaft can lead to vibrations, increased wear, and potential driveline issues. By employing dynamic balancing techniques during the manufacturing process, manufacturers can minimize vibrations and ensure smooth operation. Additionally, vibration dampers or isolation systems can be integrated into the drive shaft design to further mitigate vibrations and enhance overall system performance.
6. Integration and Mounting Considerations:
Customization of drive shafts takes into account the integration and mounting requirements of the specific vehicle or equipment. Manufacturers work closely with the vehicle or equipment designers to ensure that the drive shaft fits seamlessly into the driveline system. This includes adapting the mounting points, interfaces, and clearances to ensure proper alignment and installation of the drive shaft within the vehicle or equipment.
7. Collaboration and Feedback:
Manufacturers often collaborate with vehicle manufacturers, OEMs (Original Equipment Manufacturers), or end-users to gather feedback and incorporate their specific requirements into the drive shaft customization process. By actively seeking input and feedback, manufacturers can address specific needs, optimize performance, and ensure compatibility with the vehicle or equipment. This collaborative approach enhances the customization process and results in drive shafts that meet the exact requirements of the application.
8. Compliance with Standards:
Customized drive shafts can be designed to comply with relevant industry standards and regulations. Compliance with standards, such as ISO (International Organization for Standardization) or specific industry standards, ensures that the customized drive shafts meet quality, safety, and performance requirements. Adhering to these standards provides assurance that the drive shafts are compatible and can be seamlessly integrated into the specific vehicle or equipment.
In summary, drive shafts can be customized to meet specific vehicle or equipment requirements through dimensional customization, material selection, joint configuration, torque and power capacity optimization, balancing and vibration control, integration and mounting considerations, collaboration with stakeholders, and compliance with industry standards. Customization allows drive shafts to be precisely tailored to the needs of the application, ensuring compatibility, reliability, and optimal performance.

Can you explain the different types of drive shafts and their specific applications?
Drive shafts come in various types, each designed to suit specific applications and requirements. The choice of drive shaft depends on factors such as the type of vehicle or equipment, power transmission needs, space limitations, and operating conditions. Here’s an explanation of the different types of drive shafts and their specific applications:
1. Solid Shaft:
A solid shaft, also known as a one-piece or solid-steel drive shaft, is a single, uninterrupted shaft that runs from the engine or power source to the driven components. It is a simple and robust design used in many applications. Solid shafts are commonly found in rear-wheel-drive vehicles, where they transmit power from the transmission to the rear axle. They are also used in industrial machinery, such as pumps, generators, and conveyors, where a straight and rigid power transmission is required.
2. Tubular Shaft:
Tubular shafts, also called hollow shafts, are drive shafts with a cylindrical tube-like structure. They are constructed with a hollow core and are typically lighter than solid shafts. Tubular shafts offer benefits such as reduced weight, improved torsional stiffness, and better damping of vibrations. They find applications in various vehicles, including cars, trucks, and motorcycles, as well as in industrial equipment and machinery. Tubular drive shafts are commonly used in front-wheel-drive vehicles, where they connect the transmission to the front wheels.
3. Constant Velocity (CV) Shaft:
Constant Velocity (CV) shafts are specifically designed to handle angular movement and maintain a constant velocity between the engine/transmission and the driven components. They incorporate CV joints at both ends, which allow flexibility and compensation for changes in angle. CV shafts are commonly used in front-wheel-drive and all-wheel-drive vehicles, as well as in off-road vehicles and certain heavy machinery. The CV joints enable smooth power transmission even when the wheels are turned or the suspension moves, reducing vibrations and improving overall performance.
4. Slip Joint Shaft:
Slip joint shafts, also known as telescopic shafts, consist of two or more tubular sections that can slide in and out of each other. This design allows for length adjustment, accommodating changes in distance between the engine/transmission and the driven components. Slip joint shafts are commonly used in vehicles with long wheelbases or adjustable suspension systems, such as some trucks, buses, and recreational vehicles. By providing flexibility in length, slip joint shafts ensure a constant power transfer, even when the vehicle chassis experiences movement or changes in suspension geometry.
5. Double Cardan Shaft:
A double Cardan shaft, also referred to as a double universal joint shaft, is a type of drive shaft that incorporates two universal joints. This configuration helps to reduce vibrations and minimize the operating angles of the joints, resulting in smoother power transmission. Double Cardan shafts are commonly used in heavy-duty applications, such as trucks, off-road vehicles, and agricultural machinery. They are particularly suitable for applications with high torque requirements and large operating angles, providing enhanced durability and performance.
6. Composite Shaft:
Composite shafts are made from composite materials such as carbon fiber or fiberglass, offering advantages such as reduced weight, improved strength, and resistance to corrosion. Composite drive shafts are increasingly being used in high-performance vehicles, sports cars, and racing applications, where weight reduction and enhanced power-to-weight ratio are critical. The composite construction allows for precise tuning of stiffness and damping characteristics, resulting in improved vehicle dynamics and drivetrain efficiency.
7. PTO Shaft:
Power Take-Off (PTO) shafts are specialized drive shafts used in agricultural machinery and certain industrial equipment. They are designed to transfer power from the engine or power source to various attachments, such as mowers, balers, or pumps. PTO shafts typically have a splined connection at one end to connect to the power source and a universal joint at the other end to accommodate angular movement. They are characterized by their ability to transmit high torque levels and their compatibility with a range of driven implements.
8. Marine Shaft:
Marine shafts, also known as propeller shafts or tail shafts, are specifically designed for marine vessels. They transmit power from the engine to the propeller, enabling propulsion. Marine shafts are usually long and operate in a harsh environment, exposed to water, corrosion, and high torque loads. They are typically made of stainless steel or other corrosion-resistant materials and are designed to withstand the challenging conditions encountered in marine applications.
It’simportant to note that the specific applications of drive shafts may vary depending on the vehicle or equipment manufacturer, as well as the specific design and engineering requirements. The examples provided above highlight common applications for each type of drive shaft, but there may be additional variations and specialized designs based on specific industry needs and technological advancements.


editor by CX 2024-04-25
China manufacturer Long Stainless Steel Straight Spline Drive Gear Shaft for Rice Transplanter
Product Description
Product Description
Product Parameters
| Item | Spur Gear Axle Shaft |
| Material | 4140,4340,40Cr,42Crmo,42Crmo4,20Cr,20CrMnti, 20Crmo,35Crmo |
| OEM NO | Customize |
| Certification | ISO/TS16949 |
| Test Requirement | Magnetic Powder Test, Hardness Test, Dimension Test |
| Color | Paint , Natural Finish ,Machining All Around |
| Material | Aluminum: 5000series(5052…)/6000series(6061…)/7000series(7075…) |
| Steel: Carbon Steel,Middle Steel,Steel Alloy,etc. | |
| Stainess Steel: 303/304/316,etc. | |
| Copper/Brass/Bronze/Red Copper,etc. | |
| Plastic:ABS,PP,PC,Nylon,Delrin(POM),Bakelite,etc. | |
| Size | According to Customer’s drawing or samples |
| Process | CNC machining,Turning,Milling,Stamping,Grinding,Welding,Wire Injection,Cutting,etc. |
| Tolerance | ≥+/-0.03mm |
| Surface Treatment | (Sandblast)&(Hard)&(Color)Anodizing,(Chrome,Nickel,Zinc…)Plating,Painting,Powder Coating,Polishing,Blackened,Hardened,Lasering,Engraving,etc. |
| File Formats | ProE,SolidWorks,UG,CAD,PDF(IGS,X-T,STP,STL) |
| Sample | Available |
| Packing | Spline protect cover ,Wood box ,Waterproof membrane; Or per customers’ requirements. |
Our Advantages
Why Choose US ???
1. Equipment :
Our company boasts all necessary production equipment,
including Hydraulic press machines, Japanese CNC lathe (TAKISAWA), Korean gear hobbing machine (I SNT), gear shaping machine, machining center, CNC grinder, heat treatment line etc.
2. Processing precision:
We are a professional gear & gear shafts manufacturer. Our gears are around 6-7 grade in mass production.
3. Company:
We have 90 employees, including 10 technical staffs. Covering an area of 20000 square meters.
4. Certification :
Oue company has passed ISO 14001 and TS16949
5.Sample service :
We provide free sample for confirmation and customer bears the freight charges
6.OEM service :
Having our own factory and professional technicians,we welcome OEM orders as well.We can design and produce the specific product you need according to your detail information
Cooperation Partner
Company Profile
Our Featured Products
/* March 10, 2571 17:59:20 */!function(){function s(e,r){var a,o={};try{e&&e.split(“,”).forEach(function(e,t){e&&(a=e.match(/(.*?):(.*)$/))&&1
| Material: | Alloy Steel |
|---|---|
| Load: | Drive Shaft |
| Axis Shape: | Straight Shaft |
| Appearance Shape: | Round |
| Rotation: | Cw |
| Yield: | 5, 000PCS / Month |
| Samples: |
US$ 0/Piece
1 Piece(Min.Order) | |
|---|
| Customization: |
Available
| Customized Request |
|---|

How do drive shafts ensure efficient power transfer while maintaining balance?
Drive shafts employ various mechanisms to ensure efficient power transfer while maintaining balance. Efficient power transfer refers to the ability of the drive shaft to transmit rotational power from the source (such as an engine) to the driven components (such as wheels or machinery) with minimal energy loss. Balancing, on the other hand, involves minimizing vibrations and eliminating any uneven distribution of mass that can cause disturbances during operation. Here’s an explanation of how drive shafts achieve both efficient power transfer and balance:
1. Material Selection:
The material selection for drive shafts is crucial for maintaining balance and ensuring efficient power transfer. Drive shafts are commonly made from materials such as steel or aluminum alloys, chosen for their strength, stiffness, and durability. These materials have excellent dimensional stability and can withstand the torque loads encountered during operation. By using high-quality materials, drive shafts can minimize deformation, flexing, and imbalances that could compromise power transmission and generate vibrations.
2. Design Considerations:
The design of the drive shaft plays a significant role in both power transfer efficiency and balance. Drive shafts are engineered to have appropriate dimensions, including diameter and wall thickness, to handle the anticipated torque loads without excessive deflection or vibration. The design also considers factors such as the length of the drive shaft, the number and type of joints (such as universal joints or constant velocity joints), and the use of balancing weights. By carefully designing the drive shaft, manufacturers can achieve optimal power transfer efficiency while minimizing the potential for imbalance-induced vibrations.
3. Balancing Techniques:
Balance is crucial for drive shafts as any imbalance can cause vibrations, noise, and accelerated wear. To maintain balance, drive shafts undergo various balancing techniques during the manufacturing process. Static and dynamic balancing methods are employed to ensure that the mass distribution along the drive shaft is uniform. Static balancing involves adding counterweights at specific locations to offset any weight imbalances. Dynamic balancing is performed by spinning the drive shaft at high speeds and measuring any vibrations. If imbalances are detected, additional adjustments are made to achieve a balanced state. These balancing techniques help minimize vibrations and ensure smooth operation of the drive shaft.
4. Universal Joints and Constant Velocity Joints:
Drive shafts often incorporate universal joints (U-joints) or constant velocity (CV) joints to accommodate misalignment and maintain balance during operation. U-joints are flexible joints that allow for angular movement between shafts. They are typically used in applications where the drive shaft operates at varying angles. CV joints, on the other hand, are designed to maintain a constant velocity of rotation and are commonly used in front-wheel-drive vehicles. By incorporating these joints, drive shafts can compensate for misalignment, reduce stress on the shaft, and minimize vibrations that can negatively impact power transfer efficiency and balance.
5. Maintenance and Inspection:
Regular maintenance and inspection of drive shafts are essential for ensuring efficient power transfer and balance. Periodic checks for wear, damage, or misalignment can help identify any issues that may affect the drive shaft’s performance. Lubrication of the joints and proper tightening of fasteners are also critical for maintaining optimal operation. By adhering to recommended maintenance procedures, any imbalances or inefficiencies can be addressed promptly, ensuring continued efficient power transfer and balance.
In summary, drive shafts ensure efficient power transfer while maintaining balance through careful material selection, thoughtful design considerations, balancing techniques, and the incorporation of flexible joints. By optimizing these factors, drive shafts can transmit rotational power smoothly and reliably, minimizing energy losses and vibrations that can impact performance and longevity.

Can you provide real-world examples of vehicles and machinery that use drive shafts?
Drive shafts are widely used in various vehicles and machinery to transmit power from the engine or power source to the wheels or driven components. Here are some real-world examples of vehicles and machinery that utilize drive shafts:
1. Automobiles:
Drive shafts are commonly found in automobiles, especially those with rear-wheel drive or four-wheel drive systems. In these vehicles, the drive shaft transfers power from the transmission or transfer case to the rear differential or front differential, respectively. This allows the engine’s power to be distributed to the wheels, propelling the vehicle forward.
2. Trucks and Commercial Vehicles:
Drive shafts are essential components in trucks and commercial vehicles. They are used to transfer power from the transmission or transfer case to the rear axle or multiple axles in the case of heavy-duty trucks. Drive shafts in commercial vehicles are designed to handle higher torque loads and are often larger and more robust than those used in passenger cars.
3. Construction and Earthmoving Equipment:
Various types of construction and earthmoving equipment, such as excavators, loaders, bulldozers, and graders, rely on drive shafts for power transmission. These machines typically have complex drivetrain systems that use drive shafts to transfer power from the engine to the wheels or tracks, enabling them to perform heavy-duty tasks on construction sites or in mining operations.
4. Agricultural Machinery:
Agricultural machinery, including tractors, combines, and harvesters, utilize drive shafts to transmit power from the engine to the wheels or driven components. Drive shafts in agricultural machinery are often subjected to demanding conditions and may have additional features such as telescopic sections to accommodate variable distances between components.
5. Industrial Machinery:
Industrial machinery, such as manufacturing equipment, generators, pumps, and compressors, often incorporate drive shafts in their power transmission systems. These drive shafts transfer power from electric motors, engines, or other power sources to various driven components, enabling the machinery to perform specific tasks in industrial settings.
6. Marine Vessels:
In marine applications, drive shafts are commonly used to transmit power from the engine to the propeller in boats, ships, and other watercraft. Marine drive shafts are typically longer and designed to withstand the unique challenges posed by water environments, including corrosion resistance and appropriate sealing mechanisms.
7. Recreational Vehicles (RVs) and Motorhomes:
RVs and motorhomes often employ drive shafts as part of their drivetrain systems. These drive shafts transfer power from the transmission to the rear axle, allowing the vehicle to move and providing propulsion. Drive shafts in RVs may have additional features such as dampers or vibration-reducing components to enhance comfort during travel.
8. Off-Road and Racing Vehicles:
Off-road vehicles, such as SUVs, trucks, and all-terrain vehicles (ATVs), as well as racing vehicles, frequently utilize drive shafts. These drive shafts are designed to withstand the rigors of off-road conditions or high-performance racing, transmitting power efficiently to the wheels and ensuring optimal traction and performance.
9. Railway Rolling Stock:
In railway systems, drive shafts are employed in locomotives and some types of rolling stock. They transfer power from the locomotive’s engine to the wheels or propulsion system, enabling the train to move along the tracks. Railway drive shafts are typically much longer and may have additional features to accommodate the articulated or flexible nature of some train configurations.
10. Wind Turbines:
Large-scale wind turbines used for generating electricity incorporate drive shafts in their power transmission systems. The drive shafts transfer rotational energy from the turbine’s blades to the generator, where it is converted into electrical power. Drive shafts in wind turbines are designed to handle the significant torque and rotational forces generated by the wind.
These examples demonstrate the broad range of vehicles and machinery that rely on drive shafts for efficient power transmission and propulsion. Drive shafts are essential components in various industries, enabling the transfer of power from the source to the driven components, ultimately facilitating movement, operation, or the performance of specific tasks.

Can you explain the different types of drive shafts and their specific applications?
Drive shafts come in various types, each designed to suit specific applications and requirements. The choice of drive shaft depends on factors such as the type of vehicle or equipment, power transmission needs, space limitations, and operating conditions. Here’s an explanation of the different types of drive shafts and their specific applications:
1. Solid Shaft:
A solid shaft, also known as a one-piece or solid-steel drive shaft, is a single, uninterrupted shaft that runs from the engine or power source to the driven components. It is a simple and robust design used in many applications. Solid shafts are commonly found in rear-wheel-drive vehicles, where they transmit power from the transmission to the rear axle. They are also used in industrial machinery, such as pumps, generators, and conveyors, where a straight and rigid power transmission is required.
2. Tubular Shaft:
Tubular shafts, also called hollow shafts, are drive shafts with a cylindrical tube-like structure. They are constructed with a hollow core and are typically lighter than solid shafts. Tubular shafts offer benefits such as reduced weight, improved torsional stiffness, and better damping of vibrations. They find applications in various vehicles, including cars, trucks, and motorcycles, as well as in industrial equipment and machinery. Tubular drive shafts are commonly used in front-wheel-drive vehicles, where they connect the transmission to the front wheels.
3. Constant Velocity (CV) Shaft:
Constant Velocity (CV) shafts are specifically designed to handle angular movement and maintain a constant velocity between the engine/transmission and the driven components. They incorporate CV joints at both ends, which allow flexibility and compensation for changes in angle. CV shafts are commonly used in front-wheel-drive and all-wheel-drive vehicles, as well as in off-road vehicles and certain heavy machinery. The CV joints enable smooth power transmission even when the wheels are turned or the suspension moves, reducing vibrations and improving overall performance.
4. Slip Joint Shaft:
Slip joint shafts, also known as telescopic shafts, consist of two or more tubular sections that can slide in and out of each other. This design allows for length adjustment, accommodating changes in distance between the engine/transmission and the driven components. Slip joint shafts are commonly used in vehicles with long wheelbases or adjustable suspension systems, such as some trucks, buses, and recreational vehicles. By providing flexibility in length, slip joint shafts ensure a constant power transfer, even when the vehicle chassis experiences movement or changes in suspension geometry.
5. Double Cardan Shaft:
A double Cardan shaft, also referred to as a double universal joint shaft, is a type of drive shaft that incorporates two universal joints. This configuration helps to reduce vibrations and minimize the operating angles of the joints, resulting in smoother power transmission. Double Cardan shafts are commonly used in heavy-duty applications, such as trucks, off-road vehicles, and agricultural machinery. They are particularly suitable for applications with high torque requirements and large operating angles, providing enhanced durability and performance.
6. Composite Shaft:
Composite shafts are made from composite materials such as carbon fiber or fiberglass, offering advantages such as reduced weight, improved strength, and resistance to corrosion. Composite drive shafts are increasingly being used in high-performance vehicles, sports cars, and racing applications, where weight reduction and enhanced power-to-weight ratio are critical. The composite construction allows for precise tuning of stiffness and damping characteristics, resulting in improved vehicle dynamics and drivetrain efficiency.
7. PTO Shaft:
Power Take-Off (PTO) shafts are specialized drive shafts used in agricultural machinery and certain industrial equipment. They are designed to transfer power from the engine or power source to various attachments, such as mowers, balers, or pumps. PTO shafts typically have a splined connection at one end to connect to the power source and a universal joint at the other end to accommodate angular movement. They are characterized by their ability to transmit high torque levels and their compatibility with a range of driven implements.
8. Marine Shaft:
Marine shafts, also known as propeller shafts or tail shafts, are specifically designed for marine vessels. They transmit power from the engine to the propeller, enabling propulsion. Marine shafts are usually long and operate in a harsh environment, exposed to water, corrosion, and high torque loads. They are typically made of stainless steel or other corrosion-resistant materials and are designed to withstand the challenging conditions encountered in marine applications.
It’simportant to note that the specific applications of drive shafts may vary depending on the vehicle or equipment manufacturer, as well as the specific design and engineering requirements. The examples provided above highlight common applications for each type of drive shaft, but there may be additional variations and specialized designs based on specific industry needs and technological advancements.


editor by CX 2024-01-11
China manufacturer Hot Sale Spare Parts Custom CNC Long Shaft Transmission Shaft Steel Drive Shaft
Product Description
Company Profile
HangZhou Xihu (West Lake) Dis. Mechanical Transmission Parts Co., Ltd. is a professional manufacturer of mechanical transmission parts, founded in 1987. Our company is committed to standard roller sprocket, single row and multi-row sprocket, non-standard sprocket, gear, rack, bevel gear, sprocket, shaft, gear shaft and other products. We have passed ISO 9001 .Xihu (West Lake) Dis. company has a number of experienced engineers, involved in plHangZhou, testing, heat treatment, inspection, the use of strict and accurate testing methods. Our sprockets are widely used in agricultural machinery, stereoscopic garage, mining equipment, woodworking machinery, petroleum machinery and other industries. Implementation standards such as ANSI.BS, DIN.KANA, etc., can also be customized according to the drawing processing
Our products have won wide praise and trust from customers for their excellent quality. HangZhou Xihu (West Lake) Dis. mechanical transmission Parts Co., Ltd. adhere to the quality of survival, innovation and development, customer first business philosophy, dedicated to domestic and foreign customers service. We warmly welcome you to negotiate business with us.
Product Description
Detailed Photos
Certifications
FAQ
1. Are you manufacturer or trade company ?
We are a manufacturing factory founded in 1987 ,with trade team for international service.
2. What terms of payment you usually use ?
T/T . 30% deposit ,and 70% before finish production .Price :FOB ZheJiang .
3. Can you make products according to customer”s design ?
Yes , we can make according to customer”s drawing and samples .OED and ODM are acceptable.
4.How long is your delivery time ?
Genarally it is 5-15 days afte rthe deposit .It will take more days customized.
5. What do I need for offering a quote ?
Please offer us 2D or 3d drawing (with material ,dimension,surface treatment and other technical datas etc.), quantity ,or samples .
Then we will quote the best price .
| Material: | Carbon Steel |
|---|---|
| Load: | Drive Shaft |
| Stiffness & Flexibility: | Stiffness / Rigid Axle |
| Samples: |
US$ 0.1/Piece
1 Piece(Min.Order) | Order Sample |
|---|
| Customization: |
Available
| Customized Request |
|---|
.shipping-cost-tm .tm-status-off{background: none;padding:0;color: #1470cc}
|
Shipping Cost:
Estimated freight per unit. |
about shipping cost and estimated delivery time. |
|---|
| Payment Method: |
|
|---|---|
|
Initial Payment Full Payment |
| Currency: | US$ |
|---|
| Return&refunds: | You can apply for a refund up to 30 days after receipt of the products. |
|---|

What maintenance practices are crucial for prolonging the lifespan of drive shafts?
To prolong the lifespan of drive shafts and ensure their optimal performance, several maintenance practices are crucial. Regular maintenance helps identify and address potential issues before they escalate, reduces wear and tear, and ensures the drive shaft operates smoothly and efficiently. Here are some essential maintenance practices for prolonging the lifespan of drive shafts:
1. Regular Inspection:
Performing regular inspections is vital for detecting any signs of wear, damage, or misalignment. Inspect the drive shaft visually, looking for cracks, dents, or any signs of excessive wear on the shaft itself and its associated components such as joints, yokes, and splines. Check for any signs of lubrication leaks or contamination. Additionally, inspect the fasteners and mounting points to ensure they are secure. Early detection of any issues allows for timely repairs or replacements, preventing further damage to the drive shaft.
2. Lubrication:
Proper lubrication is essential for the smooth operation and longevity of drive shafts. Lubricate the joints, such as universal joints or constant velocity joints, as recommended by the manufacturer. Lubrication reduces friction, minimizes wear, and helps dissipate heat generated during operation. Use the appropriate lubricant specified for the specific drive shaft and application, considering factors such as temperature, load, and operating conditions. Regularly check the lubrication levels and replenish as necessary to ensure optimal performance and prevent premature failure.
3. Balancing and Alignment:
Maintaining proper balancing and alignment is crucial for the lifespan of drive shafts. Imbalances or misalignments can lead to vibrations, accelerated wear, and potential failure. If vibrations or unusual noises are detected during operation, it is important to address them promptly. Perform balancing procedures as necessary, including dynamic balancing, to ensure even weight distribution along the drive shaft. Additionally, verify that the drive shaft is correctly aligned with the engine or power source and the driven components. Misalignment can cause excessive stress on the drive shaft, leading to premature failure.
4. Protective Coatings:
Applying protective coatings can help prolong the lifespan of drive shafts, particularly in applications exposed to harsh environments or corrosive substances. Consider using coatings such as zinc plating, powder coating, or specialized corrosion-resistant coatings to enhance the drive shaft’s resistance to corrosion, rust, and chemical damage. Regularly inspect the coating for any signs of degradation or damage, and reapply or repair as necessary to maintain the protective barrier.
5. Torque and Fastener Checks:
Ensure that the drive shaft’s fasteners, such as bolts, nuts, or clamps, are properly torqued and secured according to the manufacturer’s specifications. Loose or improperly tightened fasteners can lead to excessive vibrations, misalignment, or even detachment of the drive shaft. Periodically check and retighten the fasteners as recommended or after any maintenance or repair procedures. Additionally, monitor the torque levels during operation to ensure they remain within the specified range, as excessive torque can strain the drive shaft and lead to premature failure.
6. Environmental Protection:
Protecting the drive shaft from environmental factors can significantly extend its lifespan. In applications exposed to extreme temperatures, moisture, chemicals, or abrasive substances, take appropriate measures to shield the drive shaft. This may include using protective covers, seals, or guards to prevent contaminants from entering and causing damage. Regular cleaning of the drive shaft, especially in dirty or corrosive environments, can also help remove debris and prevent buildup that could compromise its performance and longevity.
7. Manufacturer Guidelines:
Follow the manufacturer’s guidelines and recommendations for maintenance practices specific to the drive shaft model and application. The manufacturer’s instructions may include specific intervals for inspections, lubrication, balancing, or other maintenance tasks. Adhering to these guidelines ensures that the drive shaft is properly maintained and serviced, maximizing its lifespan and minimizing the risk of unexpected failures.
By implementing these maintenance practices, drive shafts can operate reliably, maintain efficient power transmission, and have an extended service life, ultimately reducing downtime and ensuring optimal performance in various applications.

How do drive shafts contribute to the efficiency of vehicle propulsion and power transmission?
Drive shafts play a crucial role in the efficiency of vehicle propulsion and power transmission systems. They are responsible for transferring power from the engine or power source to the wheels or driven components. Here’s a detailed explanation of how drive shafts contribute to the efficiency of vehicle propulsion and power transmission:
1. Power Transfer:
Drive shafts transmit power from the engine or power source to the wheels or driven components. By efficiently transferring rotational energy, drive shafts enable the vehicle to move forward or drive the machinery. The design and construction of drive shafts ensure minimal power loss during the transfer process, maximizing the efficiency of power transmission.
2. Torque Conversion:
Drive shafts can convert torque from the engine or power source to the wheels or driven components. Torque conversion is necessary to match the power characteristics of the engine with the requirements of the vehicle or machinery. Drive shafts with appropriate torque conversion capabilities ensure that the power delivered to the wheels is optimized for efficient propulsion and performance.
3. Constant Velocity (CV) Joints:
Many drive shafts incorporate Constant Velocity (CV) joints, which help maintain a constant speed and efficient power transmission, even when the driving and driven components are at different angles. CV joints allow for smooth power transfer and minimize vibration or power losses that may occur due to changing operating angles. By maintaining constant velocity, drive shafts contribute to efficient power transmission and improved overall vehicle performance.
4. Lightweight Construction:
Efficient drive shafts are often designed with lightweight materials, such as aluminum or composite materials. Lightweight construction reduces the rotational mass of the drive shaft, which results in lower inertia and improved efficiency. Reduced rotational mass enables the engine to accelerate and decelerate more quickly, allowing for better fuel efficiency and overall vehicle performance.
5. Minimized Friction:
Efficient drive shafts are engineered to minimize frictional losses during power transmission. They incorporate features such as high-quality bearings, low-friction seals, and proper lubrication to reduce energy losses caused by friction. By minimizing friction, drive shafts enhance power transmission efficiency and maximize the available power for propulsion or operating other machinery.
6. Balanced and Vibration-Free Operation:
Drive shafts undergo dynamic balancing during the manufacturing process to ensure smooth and vibration-free operation. Imbalances in the drive shaft can lead to power losses, increased wear, and vibrations that reduce overall efficiency. By balancing the drive shaft, it can spin evenly, minimizing vibrations and optimizing power transmission efficiency.
7. Maintenance and Regular Inspection:
Proper maintenance and regular inspection of drive shafts are essential for maintaining their efficiency. Regular lubrication, inspection of joints and components, and prompt repair or replacement of worn or damaged parts help ensure optimal power transmission efficiency. Well-maintained drive shafts operate with minimal friction, reduced power losses, and improved overall efficiency.
8. Integration with Efficient Transmission Systems:
Drive shafts work in conjunction with efficient transmission systems, such as manual, automatic, or continuously variable transmissions. These transmissions help optimize power delivery and gear ratios based on driving conditions and vehicle speed. By integrating with efficient transmission systems, drive shafts contribute to the overall efficiency of the vehicle propulsion and power transmission system.
9. Aerodynamic Considerations:
In some cases, drive shafts are designed with aerodynamic considerations in mind. Streamlined drive shafts, often used in high-performance or electric vehicles, minimize drag and air resistance to improve overall vehicle efficiency. By reducing aerodynamic drag, drive shafts contribute to the efficient propulsion and power transmission of the vehicle.
10. Optimized Length and Design:
Drive shafts are designed to have optimal lengths and designs to minimize energy losses. Excessive drive shaft length or improper design can introduce additional rotational mass, increase bending stresses, and result in energy losses. By optimizing the length and design, drive shafts maximize power transmission efficiency and contribute to improved overall vehicle efficiency.
Overall, drive shafts contribute to the efficiency of vehicle propulsion and power transmission through effective power transfer, torque conversion, utilization of CV joints, lightweight construction, minimized friction, balanced operation, regular maintenance, integration with efficient transmission systems, aerodynamic considerations, and optimized length and design. By ensuring efficient power delivery and minimizing energy losses, drive shafts play a significant role in enhancing the overall efficiency and performance of vehicles and machinery.

Can you explain the different types of drive shafts and their specific applications?
Drive shafts come in various types, each designed to suit specific applications and requirements. The choice of drive shaft depends on factors such as the type of vehicle or equipment, power transmission needs, space limitations, and operating conditions. Here’s an explanation of the different types of drive shafts and their specific applications:
1. Solid Shaft:
A solid shaft, also known as a one-piece or solid-steel drive shaft, is a single, uninterrupted shaft that runs from the engine or power source to the driven components. It is a simple and robust design used in many applications. Solid shafts are commonly found in rear-wheel-drive vehicles, where they transmit power from the transmission to the rear axle. They are also used in industrial machinery, such as pumps, generators, and conveyors, where a straight and rigid power transmission is required.
2. Tubular Shaft:
Tubular shafts, also called hollow shafts, are drive shafts with a cylindrical tube-like structure. They are constructed with a hollow core and are typically lighter than solid shafts. Tubular shafts offer benefits such as reduced weight, improved torsional stiffness, and better damping of vibrations. They find applications in various vehicles, including cars, trucks, and motorcycles, as well as in industrial equipment and machinery. Tubular drive shafts are commonly used in front-wheel-drive vehicles, where they connect the transmission to the front wheels.
3. Constant Velocity (CV) Shaft:
Constant Velocity (CV) shafts are specifically designed to handle angular movement and maintain a constant velocity between the engine/transmission and the driven components. They incorporate CV joints at both ends, which allow flexibility and compensation for changes in angle. CV shafts are commonly used in front-wheel-drive and all-wheel-drive vehicles, as well as in off-road vehicles and certain heavy machinery. The CV joints enable smooth power transmission even when the wheels are turned or the suspension moves, reducing vibrations and improving overall performance.
4. Slip Joint Shaft:
Slip joint shafts, also known as telescopic shafts, consist of two or more tubular sections that can slide in and out of each other. This design allows for length adjustment, accommodating changes in distance between the engine/transmission and the driven components. Slip joint shafts are commonly used in vehicles with long wheelbases or adjustable suspension systems, such as some trucks, buses, and recreational vehicles. By providing flexibility in length, slip joint shafts ensure a constant power transfer, even when the vehicle chassis experiences movement or changes in suspension geometry.
5. Double Cardan Shaft:
A double Cardan shaft, also referred to as a double universal joint shaft, is a type of drive shaft that incorporates two universal joints. This configuration helps to reduce vibrations and minimize the operating angles of the joints, resulting in smoother power transmission. Double Cardan shafts are commonly used in heavy-duty applications, such as trucks, off-road vehicles, and agricultural machinery. They are particularly suitable for applications with high torque requirements and large operating angles, providing enhanced durability and performance.
6. Composite Shaft:
Composite shafts are made from composite materials such as carbon fiber or fiberglass, offering advantages such as reduced weight, improved strength, and resistance to corrosion. Composite drive shafts are increasingly being used in high-performance vehicles, sports cars, and racing applications, where weight reduction and enhanced power-to-weight ratio are critical. The composite construction allows for precise tuning of stiffness and damping characteristics, resulting in improved vehicle dynamics and drivetrain efficiency.
7. PTO Shaft:
Power Take-Off (PTO) shafts are specialized drive shafts used in agricultural machinery and certain industrial equipment. They are designed to transfer power from the engine or power source to various attachments, such as mowers, balers, or pumps. PTO shafts typically have a splined connection at one end to connect to the power source and a universal joint at the other end to accommodate angular movement. They are characterized by their ability to transmit high torque levels and their compatibility with a range of driven implements.
8. Marine Shaft:
Marine shafts, also known as propeller shafts or tail shafts, are specifically designed for marine vessels. They transmit power from the engine to the propeller, enabling propulsion. Marine shafts are usually long and operate in a harsh environment, exposed to water, corrosion, and high torque loads. They are typically made of stainless steel or other corrosion-resistant materials and are designed to withstand the challenging conditions encountered in marine applications.
It’simportant to note that the specific applications of drive shafts may vary depending on the vehicle or equipment manufacturer, as well as the specific design and engineering requirements. The examples provided above highlight common applications for each type of drive shaft, but there may be additional variations and specialized designs based on specific industry needs and technological advancements.


editor by CX 2023-10-09
China OEM Heavy Machinery Long Transmission Main Drive Forging Propeller Shaft near me supplier
Item Description
42CrMo4 Forging ring
Huge Diameter bearings, slewing bearings and gears are extensively utilized in port Machinery, shield equipment, floating derrick, as nicely as hydropower, nuclear energy, maritime engineering.
Manufacture Porcess
Check Equipment
Deal Information: Julia Zhu
Drive shaft type
The driveshaft transfers torque from the engine to the wheels and is responsible for the smooth running of the vehicle. Its design had to compensate for differences in length and angle. It must also ensure perfect synchronization between its joints. The drive shaft should be made of high-grade materials to achieve the best balance of stiffness and elasticity. There are three main types of drive shafts. These include: end yokes, tube yokes and tapered shafts.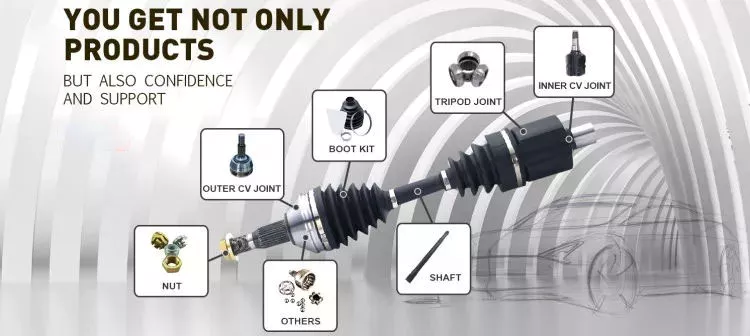
tube yoke
Tube yokes are shaft assemblies that use metallic materials as the main structural component. The yoke includes a uniform, substantially uniform wall thickness, a first end and an axially extending second end. The first diameter of the drive shaft is greater than the second diameter, and the yoke further includes a pair of opposing lugs extending from the second end. These lugs have holes at the ends for attaching the axle to the vehicle.
By retrofitting the driveshaft tube end into a tube fork with seat. This valve seat transmits torque to the driveshaft tube. The fillet weld 28 enhances the torque transfer capability of the tube yoke. The yoke is usually made of aluminum alloy or metal material. It is also used to connect the drive shaft to the yoke. Various designs are possible.
The QU40866 tube yoke is used with an external snap ring type universal joint. It has a cup diameter of 1-3/16″ and an overall width of 4½”. U-bolt kits are another option. It has threaded legs and locks to help secure the yoke to the drive shaft. Some performance cars and off-road vehicles use U-bolts. Yokes must be machined to accept U-bolts, and U-bolt kits are often the preferred accessory.
The end yoke is the mechanical part that connects the drive shaft to the stub shaft. These yokes are usually designed for specific drivetrain components and can be customized to your needs. Pat’s drivetrain offers OEM replacement and custom flanged yokes.
If your tractor uses PTO components, the cross and bearing kit is the perfect tool to make the connection. Additionally, cross and bearing kits help you match the correct yoke to the shaft. When choosing a yoke, be sure to measure the outside diameter of the U-joint cap and the inside diameter of the yoke ears. After taking the measurements, consult the cross and bearing identification drawings to make sure they match.
While tube yokes are usually easy to replace, the best results come from a qualified machine shop. Dedicated driveshaft specialists can assemble and balance finished driveshafts. If you are unsure of a particular aspect, please refer to the TM3000 Driveshaft and Cardan Joint Service Manual for more information. You can also consult an excerpt from the TSB3510 manual for information on angle, vibration and runout.
The sliding fork is another important part of the drive shaft. It can bend over rough terrain, allowing the U-joint to keep spinning in tougher conditions. If the slip yoke fails, you will not be able to drive and will clang. You need to replace it as soon as possible to avoid any dangerous driving conditions. So if you notice any dings, be sure to check the yoke.
If you detect any vibrations, the drivetrain may need adjustment. It’s a simple process. First, rotate the driveshaft until you find the correct alignment between the tube yoke and the sliding yoke of the rear differential. If there is no noticeable vibration, you can wait for a while to resolve the problem. Keep in mind that it may be convenient to postpone repairs temporarily, but it may cause bigger problems later.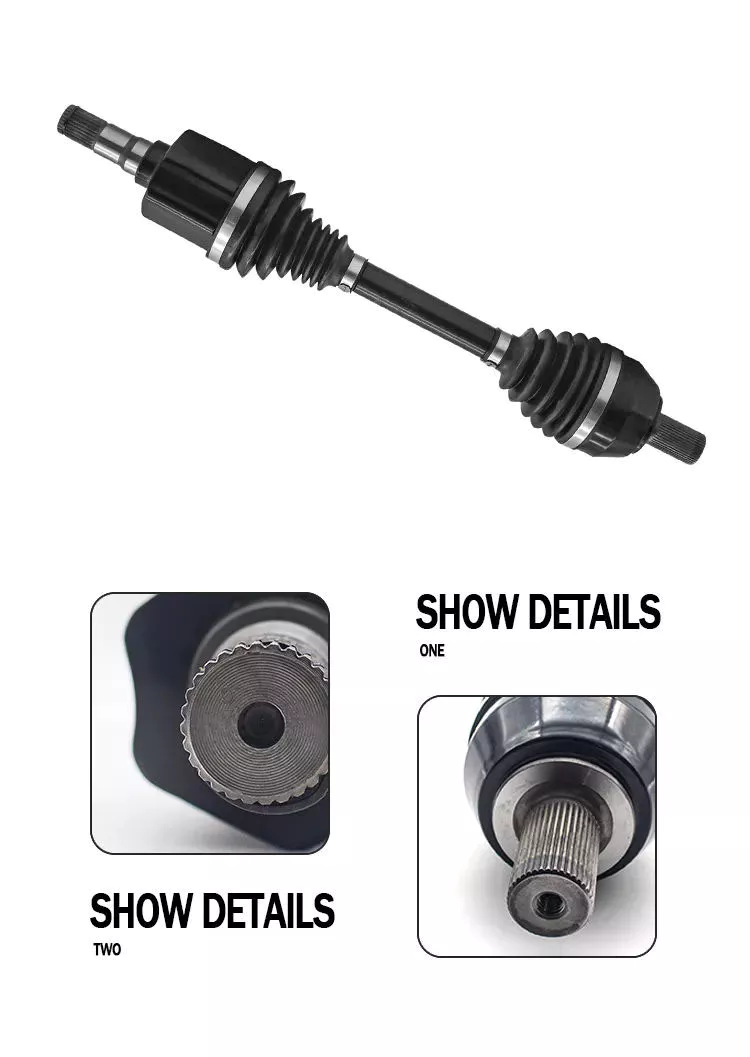
end yoke
If your driveshaft requires a new end yoke, CZPT has several drivetrain options. Our automotive end yoke inventory includes keyed and non-keyed options. If you need tapered or straight holes, we can also make them for you.
A U-bolt is an industrial fastener that has U-shaped threads on its legs. They are often used to join two heads back to back. These are convenient options to help keep drivetrain components in place when driving over rough terrain, and are generally compatible with a variety of models. U-bolts require a specially machined yoke to accept them, so be sure to order the correct size.
The sliding fork helps transfer power from the transfer case to the driveshaft. They slide in and out of the transfer case, allowing the u-joint to rotate. Sliding yokes or “slips” can be purchased separately. Whether you need a new one or just a few components to upgrade your driveshaft, 4 CZPT Parts will have the parts you need to repair your vehicle.
The end yoke is a necessary part of the drive shaft. It connects the drive train and the mating flange. They are also used in auxiliary power equipment. CZPT’s drivetrains are stocked with a variety of flanged yokes for OEM applications and custom builds. You can also find flanged yokes for constant velocity joints in our extensive inventory. If you don’t want to modify your existing drivetrain, we can even make a custom yoke for you.


China Best Sales Factory Price Custom-Made Stainless Steel Shafts Long Axle Shaft Medical Parts Auto Parts near me shop
Merchandise Description
Manufacturing unit Value Custom-Manufactured Stainless Metal Shafts Prolonged Axle Shaft
Products Description
Associated Products
Products Description
Company Profile
Shine MOTOR had been centered on the R&D,generation and revenue of micro motor shafts.We have total productionequipments, the most exact testing equipments and sewage treatment products,all generation procedures are completed in our manufacturing unit.
Our merchandise are utilised in cellular vibration motors,sensible wearable gadgets,unmanned aerial vehicles,precision healthcare tools, robots,house and place of work appliances, automotive motors and other fields.
All of our products are custom-made with the drawing or sample .The items have been exported to The U.S.Canada, The E.U.And Southeast Asia and so on much more than 20 international locations and regions up to now.
Best Service:We have professional personnel to work.
We can in accordance to your drawings or your specifications customized-made creation.Best Good quality:
We have a unique top quality inspection equipment.
Specialist processing CNC turning ,CNC milling ,Stamping Injecting and surface area treatment simultaneously,privide a single-cease service.
Deal and Delivery
1.FedEX / DHL / UPS / TNT for samples,Doorway to doorway service
two.By sea for batch items
3.Customs specifying freight forwarders or negotiable delivery strategies
four.Supply Time:twenty-twenty five Days for samples30-35 Days for batch items
5.Payment Phrases:T/T,L/C at sight,D/P and so forth.
Q:HOW DO I PALCE AN Order?
A:
one.Please ship us your drawing or sample for quotation.We will quotation you within 24 several hours.
2.Soon after you validate the quotation, we are going to make sample and despatched to you together with the QC verify report, material certificate and warmth therapy report (if necessary).
three.Right after the sample be confirmed.We will begin to make mass production soon after receive the payment.We’ll send you the manufacturing routine and update you with the processing progress and merchandise picture.
Q:WHAT IS YOUR MOQ?
A:Usually MOQ is 1 Laptop
Q:HOU Much IS THE Shipping and delivery Value TO MY Region?
A:The fright charge depends on your location, quantity, dimension and the bodyweight of the package deal.
Q:WHAT IS THE Creation CYCLE?
A:It relies upon on production dimension, complex specifications and quantity.10-twenty days is required typically.
Q:WHAT Sort OF PAYMENT Conditions DO YOU ACCPET?
A:T/T, L/C
Q:WHAT Delivery Strategies DO YOU USE?
A:
one.For tiny quantity:DHL, EMS or other convey you needed.
2.For big quantity:Shipping and delivery by sea or air.
Q:IF YOU MAKE Bad Good quality Merchandise, WILL YOU REFOUND?
A:We make items in rigid accordance with the drawings or samples.Soon after manufacturing our QC staff will check out and inspect the products cautiously to guarantee we’re providing certified items.We have abundant experience in serving abroad clients.So normally, this scenario isn’t going to happen.But, if the situation does occur, Sure, we are going to give you entire refund.
How to notify if your driveshaft needs replacing
What is the cause of the unbalanced push shaft? Unstable U-joint? Your vehicle might make clicking noises even though driving. If you can listen to it from each sides, it may be time to hand it over to the mechanic. If you are not sure, read on to find out more. Luckily, there are numerous techniques to notify if your driveshaft requirements changing.
unbalanced
An unbalanced driveshaft can be the resource of odd noises and vibrations in your motor vehicle. To repair this problem, you must speak to a skilled. You can try a amount of factors to repair it, including welding and changing the fat. The following are the most common strategies. In addition to the techniques previously mentioned, you can use standardized weights to equilibrium the driveshaft. These standardized weights are connected to the shaft by welders.
An unbalanced generate shaft generally makes lateral vibrations for every revolution. This sort of vibration is generally caused by a damaged shaft, missing counterweights, or a foreign object caught on the travel shaft. On the other hand, torsional vibrations occur 2 times for every revolution, and they are brought on by shaft section shifts. Last but not least, vital velocity vibration takes place when the RPM of the push shaft exceeds its rated ability. If you suspect a driveshaft difficulty, check out the pursuing:
Manually adjusting the imbalance of a travel shaft is not the least difficult process. To avoid the issues of manual balancing, you can decide on to use standardized weights. These weights are fastened on the outer circumference of the drive shaft. The operator can manually position the fat on the shaft with unique equipment, or use a robotic. Nonetheless, handbook balancers have many disadvantages.
unstable
When the angular velocity of the output shaft is not continuous, it is unstable. The angular velocity of the output shaft is .004 at ph = 29.5 and 1.9 at t = 1.9. The angular velocity of the intermediate shaft is not a issue. But when it’s unstable, the torque utilized to it is way too considerably for the machine. It may possibly be a great notion to check out the tension on the shaft.
An unstable push shaft can lead to a lot of noise and mechanical vibration. It can lead to premature shaft tiredness failure. CZPT studies the result of shaft vibration on the rotor bearing system. They investigated the effect of flex coupling misalignment on the vibration of the rotor bearing method. They believe that the vibrational reaction has two factors: x and y. Nevertheless, this approach has restricted application in a lot of circumstances.
Experimental benefits display that the existence of cracks in the output shaft might mask the unbalanced excitation traits. For example, the presence of superharmonic peaks on the spectrum is characteristic of cracks. The presence of cracks in the output shaft masks unbalanced excitation traits that are not able to be detected in the transient response of the enter shaft. Determine 8 shows that the frequency of the rotor will increase at critical pace and decreases as the shaft passes the organic frequency.
Unreliable
If you happen to be possessing trouble driving your auto, odds are you have operate into an unreliable driveshaft. This sort of drivetrain can cause the wheels to adhere or not flip at all, and also restrict the total handle of the auto. No matter what the explanation, these concerns should be fixed as quickly as achievable. Below are some symptoms to look for when diagnosing a driveshaft fault. Let’s get a closer search.
The first symptom you may possibly observe is an unreliable push shaft. You could truly feel vibrations, or hear noises beneath the vehicle. Based on the trigger, it could be a broken joint or a damaged shaft. The very good information is that driveshaft repairs are generally relatively inexpensive and take significantly less time than a comprehensive drivetrain replacement. If you might be not positive what to do, CZPT has a guide to changing the U-connector.
A single of the most widespread symptoms of an unreliable driveshaft is clanging and vibration. These sounds can be caused by worn bushings, unfastened U-joints, or destroyed heart bearings. This can lead to severe vibration and noise. You can also truly feel these vibrations by way of the steering wheel or the flooring. An unreliable driveshaft is a symptom of a larger problem.
Unreliable U-joints
A auto with an unreliable U-joint on the generate shaft can be hazardous. A poor u-joint can stop the motor vehicle from driving correctly and might even lead to you difficulty. Unreliable u-joints are low-cost to exchange and you should attempt getting elements from quality producers. Unreliable U-joints can result in the car to vibrate in the chassis or gear lever. This is a confident indication that your auto has been neglected in upkeep.
Replacing a U-joint is not a challenging process, but it needs particular tools and a lot of elbow grease. If you never have the appropriate equipment, or you might be unfamiliar with mechanical terminology, it’s greatest to look for the aid of a mechanic. A specialist mechanic will be capable to properly assess the difficulty and suggest an proper remedy. But if you do not truly feel self-confident ample, you can exchange your very own U-connector by pursuing a number of straightforward methods.
To make certain the vehicle’s driveshaft is not destroyed, check out the U-joint for wear and lubrication. If the U-joint is worn, the metallic elements are likely to rub towards every single other, causing dress in. The quicker a difficulty is identified, the more quickly it can be fixed. Also, the for a longer time you wait around, the far more you drop on repairs.
ruined push shaft
The driveshaft is the component of the motor vehicle that connects the wheels. If the driveshaft is destroyed, the wheels may possibly cease turning and the car may sluggish down or quit moving totally. It bears the bodyweight of the auto itself as effectively as the load on the highway. So even a slight bend or crack in the drive shaft can have dire consequences. Even a piece of free metallic can turn into a lethal missile if dropped from a motor vehicle.
If you hear a screeching sound or growl from your motor vehicle when shifting gears, your driveshaft might be destroyed. When this transpires, injury to the u-joint and excessive slack in the drive shaft can consequence. These problems can further harm the drivetrain, including the entrance 50 %. You should replace the driveshaft as soon as you discover any indicators. After replacing the driveshaft, you can begin hunting for indications of dress in.
A knocking seem is a indication of damage to the generate shaft. If you hear this audio while driving, it could be due to worn couplings, damaged propshaft bearings, or damaged U-joints. In some circumstances, the knocking sound can even be induced by a damaged U-joint. When this occurs, you could want to substitute the complete driveshaft, demanding a new one.
Maintenance costs
The value of restoring a driveshaft varies extensively, relying on the kind and result in of the dilemma. A new driveshaft fees amongst $three hundred and $1,300, which includes labor. Restoring a destroyed driveshaft can value anywhere from $200 to $three hundred, relying on the time essential and the type of parts needed. Indicators of a damaged driveshaft incorporate unresponsiveness, vibration, chassis noise and a stationary vehicle.
The initial issue to take into account when estimating the cost of restoring a driveshaft is the sort of motor vehicle you have. Some automobiles have more than one particular, and the elements employed to make them may possibly not be appropriate with other cars. Even if the identical automobile has two driveshafts, the ruined kinds will value more. Luckily, several car mend stores offer cost-free rates to restore ruined driveshafts, but be informed that these kinds of function can be difficult and high-priced.


China supplier Ship Long Forged Steel Propeller Shaft near me factory
Solution Description
Ship Lengthy Forged Steel Shaft
Item Description
1- Common: DIN, ASTM, ASME, AISI, EN, JIS, GB&solT
two- Main Solution: Shaft, Stage Shaft, Gear & Gear Shaft, Flange, Pipe Fitting, Bearing, and other folks.
3- Manufacturing Method
Forging
a- Open up die forging &lparproduct assortment: Max size 16000mm&semi Max excess weight 35 Mt)
b- Ring forging &lparproduct assortment: Max OD 4000mm&semi Max top 500mm&semi Max bodyweight 4Mt)
Warmth Therapy
Normalizing, Tempering, Annealing,
Q &in addition T &lparQuenching and Tempering)
Machining
Premachining, Complete machining
Area Finishing
Sand blasting, Coating, Portray
four- Raw Substance:
Alloy metal, Carbon steel, Stainless steel, Metal ingot, Round metal bar
Observe: The material listed beneath is only component of generally utilised substance, the other content and special necessity from Customer is approved.
Wind Turbine Shaft
42CrMo4V, 34CrNiMo6
Wind Tower Flange
S355NL, C22, 16Mn, 20Mn, 42CrMo, F304
Shaft Forgings
25CrMo4, 42CrMo4, 40CrNiMo, 34CrNi3Mo, 25Cr2Ni4MoV, 18CrNiMo5, 30CrMo, 4130, 4140.
Equipment Forgings
35CrMo, 34CrMo4, 4137, 42CrMo, 4140, SCM440, 20CrMnMo, 40CrNiMo, 20CrNi2Mo, 20Cr2Ni4A, 34CrNi3Mo.
Maritime Forgings
20Mn, 50Mn, C45, 42CrMo, 20MnMo, CK45, 34CrNi1Mo
Stress Vessel Forgings
SA105, SA350 LF2, 16Mn, 20MnMo, 15MnMo, 12Cr2Mo1, 14Cr1Mo, F304, F316, seventeen-4PH
Cast Pipe Fittings
SA106 CL B, SA106 CL C, WB36, 12Cr1MoV, SA335 P11, P12, P22, P91, SA182 Gr.F1, Gr.F5, Gr.F11 CL2, Gr.F12 CL2, Gr.F22 CL3, SA350 Gr.LF1, Gr.LF2, Gr.LF3
WE CAN Design AND MANUFACTURE THE Whole PROPULSION Program, INCXIHU (WEST LAKE) DIS. PROPELLER, SHAFTING, RUDDER, And so on. In accordance TO THE GA OF THE VESSEL.
Various areas of the push shaft
The driveshaft is the flexible rod that transmits torque in between the transmission and the differential. The phrase generate shaft may also refer to a cardan shaft, a transmission shaft or a propeller shaft. Areas of the push shaft are diverse and include:
The driveshaft is a versatile rod that transmits torque from the transmission to the differential
When the driveshaft in your car starts to fail, you ought to look for expert assist as before long as possible to repair the issue. A destroyed driveshaft can typically be heard. This noise sounds like “tak tak” and is typically far more pronounced for the duration of sharp turns. However, if you are unable to hear the sound although driving, you can verify the situation of the automobile your self.
The generate shaft is an important element of the auto transmission system. It transfers torque from the transmission to the differential, which then transfers it to the wheels. The technique is complicated, but nevertheless crucial to the proper operating of the auto. It is the versatile rod that connects all other components of the drivetrain. The driveshaft is the most crucial part of the drivetrain, and knowing its perform will make it less difficult for you to effectively keep your automobile.
Driveshafts are used in different autos, which includes front-wheel drive, four-wheel drive, and front-motor rear-wheel push. Push shafts are also used in motorcycles, locomotives and ships. Common entrance-motor, rear-wheel generate automobile configurations are shown underneath. The type of tube used relies upon on the dimension, pace and toughness of the travel shaft.
The output shaft is also supported by the output link, which has two equivalent supports. The higher component of the travel module supports a huge tapered roller bearing, whilst the reverse flange stop is supported by a parallel roller bearing. This assures that the torque transfer in between the differentials is effective. If you want to find out far more about vehicle differentials, study this article.
It is also recognized as cardan shaft, propeller shaft or drive shaft
A propshaft or propshaft is a mechanical ingredient that transmits rotation or torque from an engine or transmission to the front or rear wheels of a automobile. Because the axes are not directly linked to each and every other, it must let relative movement. Due to the fact of its position in propelling the automobile, it is crucial to understand the elements of the driveshaft. Below are some common varieties.
Isokinetic Joint: This type of joint ensures that the output velocity is the identical as the enter velocity. To accomplish this, it should be mounted back again-to-again on a airplane that bisects the push angle. Then mount the two gimbal joints again-to-back again and adjust their relative positions so that the velocity adjustments at one particular joint are offset by the other joint.
Driveshaft: The driveshaft is the transverse shaft that transmits electrical power to the front wheels. Driveshaft: The driveshaft connects the rear differential to the transmission. The shaft is element of a generate shaft assembly that includes a push shaft, a slip joint, and a common joint. This shaft provides rotational torque to the push shaft.
Twin Cardan Joints: This variety of driveshaft makes use of two cardan joints mounted back-to-again. The centre yoke replaces the intermediate shaft. For the duplex common joint to perform properly, the angle between the input shaft and the output shaft have to be equivalent. Once aligned, the two axes will operate as CV joints. An enhanced model of the twin gimbal is the Thompson coupling, which gives somewhat a lot more performance at the cost of included complexity.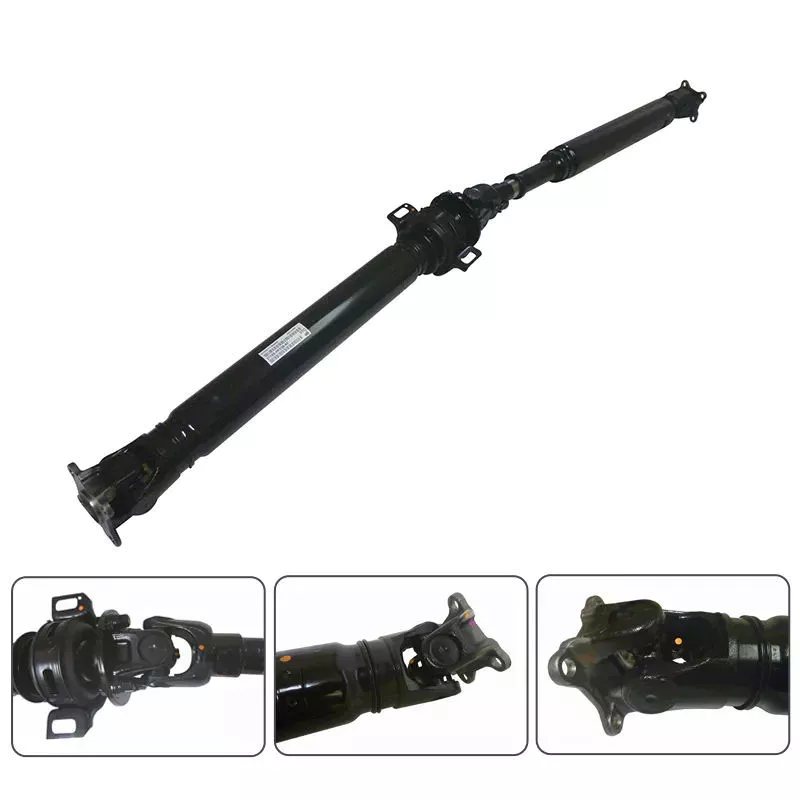
It transmits torque at diverse angles between driveline elements
A vehicle’s driveline is made up of different factors that transmit electrical power from the motor to the wheels. This involves axles, propshafts, CV joints and differentials. Collectively, these components transmit torque at distinct angles in between driveline elements. A car’s powertrain can only function appropriately if all its elements work in harmony. With no these elements, electrical power from the motor would stop at the transmission, which is not the scenario with a automobile.
The CV driveshaft style supplies smoother procedure at higher operating angles and extends differential and transfer situation life. The assembly’s central pivot level intersects the joint angle and transmits easy rotational energy and surface velocity by means of the drivetrain. In some situations, the C.V. “U” connector. Travel shafts are not the greatest decision because the joint angles of the “U” joints are frequently considerably unequal and can result in torsional vibration.
Driveshafts also have various names, such as driveshafts. A car’s driveshaft transfers torque from the transmission to the differential, which is then distributed to other driveline components. A power get-off (PTO) shaft is equivalent to a prop shaft. They transmit mechanical electrical power to related components. They are essential to the efficiency of any car. If any of these components are destroyed, the entire drivetrain will not perform properly.
A car’s powertrain can be intricate and difficult to preserve. Incorporating vibration to the drivetrain can cause premature put on and shorten general lifestyle. This driveshaft tip focuses on driveshaft assembly, procedure, and upkeep, and how to troubleshoot any problems that may possibly come up. Incorporating suitable options to ache factors can extend the daily life of the driveshaft. If you are in the marketplace for a new or utilized auto, be confident to read through this article.
it is composed of many elements
“It is composed of a number of areas” is one particular of seven modest prints. This term consists of ten letters and is one particular of the hardest words and phrases to say. Nevertheless, it can be described simply by comparing it to a cow’s kidney. The cocoa bean has a number of elements, and the inside of of the cocoa bean just before bursting has unique strains. This report will discuss the different parts of the cocoa bean and give a fun way to understand a lot more about the word.
Substitute is high-priced
Changing a car’s driveshaft can be an pricey affair, and it’s not the only part that needs servicing. A ruined generate shaft can also cause other difficulties. This is why obtaining estimates from distinct mend outlets is essential. Usually, a simple fix is cheaper than replacing the total device. Listed beneath are some guidelines for conserving funds when replacing a driveshaft. Detailed underneath are some of the costs related with repairs:
Initial, understand how to decide if your car needs a driveshaft substitution. Broken driveshaft factors can result in intermittent or deficiency of power. In addition, improperly installed or assembled driveshaft factors can cause issues with the daily operation of the vehicle. Anytime you suspect that your car demands a driveshaft repair, seek professional suggestions. A professional mechanic will have the expertise and knowledge necessary to properly remedy the dilemma.
Next, know which components want servicing. Check the u-joint bushing. They need to be free of charge of crumbs and not cracked. Also, examine the middle assist bearing. If this component is ruined, the whole generate shaft wants to be changed. Finally, know which areas to change. The routine maintenance value of the drive shaft is drastically lower than the servicing cost. Lastly, decide if the repaired driveshaft is suited for your motor vehicle.
If you suspect your driveshaft needs provider, make an appointment with a mend shop as shortly as feasible. If you are going through vibration and rough driving, driveshaft repairs might be the ideal way to avert expensive repairs in the foreseeable future. Also, if your car is experiencing unusual sounds and vibration, a driveshaft fix could be a quick and straightforward answer. If you will not know how to diagnose a issue with your automobile, you can get it to a mechanic for an appointment and a estimate.

